Herpes is a common viral infection that affects millions of people worldwide. In this article, we aim to shed light on herpes, its causes, symptoms, and preventive measures.
What is Herpes?
Herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). There are two main types of herpes viruses: HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 is primarily associated with oral herpes, causing cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth and on the face. HSV-2, on the other hand, is linked to genital herpes, a sexually transmitted infection affecting the genital and anal areas.
Causes of Herpes:
Herpes is primarily transmitted through direct contact with an infected person’s skin, mucous membranes, or bodily fluids. This can occur during sexual activity, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. However, it’s important to note that herpes can also be transmitted through non-sexual means, such as kissing or sharing personal items like towels or razors.
Symptoms of Herpes:
The symptoms of herpes can vary depending on the type of virus and the location of the infection. Common symptoms include:
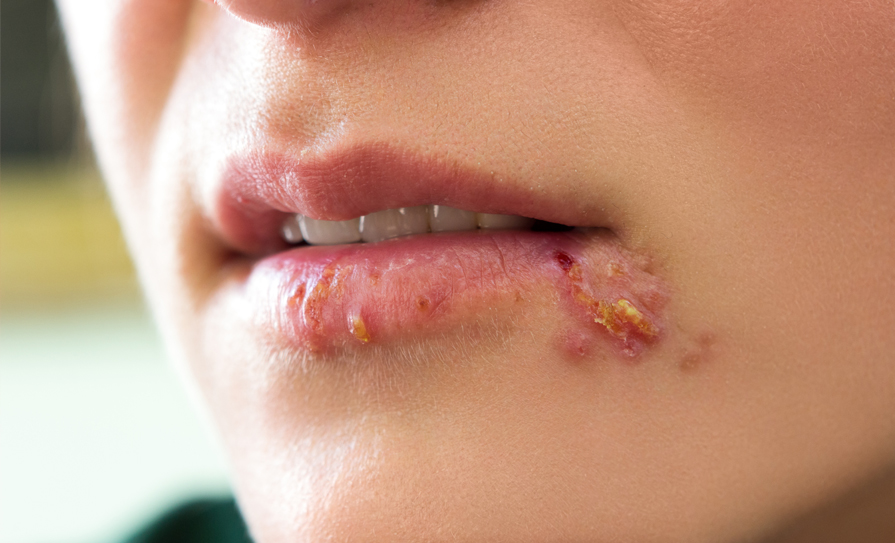
Oral Herpes (HSV-1):
Cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth or on the face.
Itching, burning, or tingling sensations before the appearance of sores.
Genital Herpes (HSV-2):
Pain, itching, or tingling in the genital or anal area.
Small red bumps, blisters, or open sores in the genital or anal region.
Flu-like symptoms, including fever and swollen lymph nodes.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) an estimated 3.7 billion people under age 50 (67%) globally have herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) infection, the main cause of oral herpes.
Prevention and Management
Safe Practices:
- Practice safe sex by using condoms or dental dams during sexual activity.
- Be aware of your partner’s sexual health and communicate openly about STIs.
Avoiding Contact:
- Avoid intimate contact with individuals during an active outbreak.
- Refrain from sharing personal items that may come into contact with the infected area.
Antiviral Medications:
- Antiviral medications can help manage and reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
- Consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment options.
Regular Check-ups:
- Attend regular sexual health check-ups, especially if you are sexually active.
As recommended by the World Health Organization, people with symptoms suggestive of genital herpes should be offered HIV testing while pregnant women with symptoms of genital herpes should inform their health care providers. Preventing acquisition of HSV-2 infection is particularly important for women in late pregnancy when the risk for neonatal herpes is greatest.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends taking anti-herpes medicine towards the end of the pregnancy. This medicine may reduce the risk of having signs or symptoms of genital herpes when the pregnant woman delivers.
Conclusion
Herpes is a common yet manageable condition. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can minimize the risk of transmission and effectively manage the virus. Open communication about sexual health, regular check-ups, and safe practices contribute to a healthier and informed society.
It is always important to seek medical advice from healthcare professionals as it is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans.

Great post