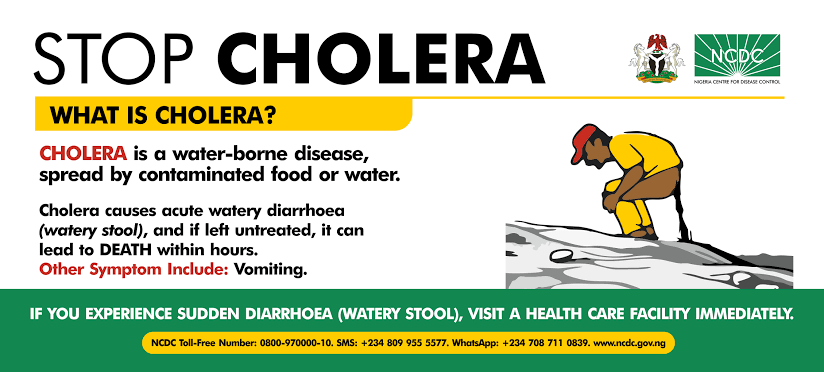
Overview:
Cholera is an acute diarrheal infection caused by ingestion of food or water contaminated with the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. It can cause severe dehydration and can be fatal if left untreated.
Prevention:
- Safe Water and Sanitation: Ensure access to safe drinking water and proper sanitation facilities. Boil or treat water before drinking.
- Hygiene Practices: Regular handwashing with soap, especially after using the toilet and before handling food.
- Food Safety: Consume well-cooked food, avoid raw or undercooked seafood, and maintain clean food preparation areas.
- Vaccination: In high-risk areas, cholera vaccines can be administered as a preventive measure.
Treatment and Care:
- Rehydration: Immediate rehydration is crucial. Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS) solution is the most effective way to treat dehydration. In severe cases, intravenous fluids may be necessary.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics can reduce the duration of diarrhea and the volume of rehydration fluids needed.
- Zinc Supplements: Zinc supplements are beneficial, particularly for children, to reduce the duration and severity of the disease.
- Continued Nutrition: Encourage continued feeding of affected individuals, especially children, to prevent malnutrition.
In light of the recent cholera outbreak in Lagos State, Nigeria, it is essential to stay informed and take preventive measures seriously.
For more detailed information, visit:
https://ncdc.gov.ng/diseases/info/C
